Glia, September 2014
Early phenotypic asymmetry of sister oligodendrocyte progenitor cells after mitosis and its modulation by aging and extrinsic factors
Enrica Boda, 1 Silvia Di Maria, 1 Patrizia Rosa, 2 Verdon Taylor, 3 Maria P. Abbracchio, 4 and Annalisa Buffo 1
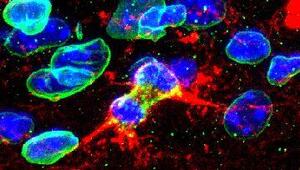
Oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs) persist in the adult central nervous system and guarantee oligodendrocyte turnover xthroughout life. It remains obscure how OPCs avoid exhaustion during adulthood. Similar to stem cells, OPCs could self-maintain by undergoing asymmetric divisions generating a mixed progeny either keeping a progenitor phenotype or proceeding to differentiation.
To address this issue, we examined the distribution of stage-specific markers in sister OPCs during mitosis and later after cell birth, and assessed its correlation with distinct short-term fates. In both the adult and juvenile cerebral cortex a fraction of dividing OPCs gives rise to sister cells with diverse immunophenotypic profiles and short-term behaviors. Such heterogeneity appears as cells exit cytokinesis, but does not derive from the asymmetric segregation of molecules such as NG2 or PDGFRa expressed in the mother cell. Rather, rapid downregulation of OPC markers and upregulation of molecules associated with lineage progression contributes to generate early sister OPC asymmetry.
Analyses during aging and upon exposure to physiological (i.e., increased motor activity) and pathological (i.e., trauma or demyelination) stimuli showed that both intrinsic and environmental factors contribute to determine the fraction of symmetric and asymmetric OPC pairs and the phenotype of the OPC progeny as soon as cells exit mitosis. [ read more ]
In the photo, starting from the left: Annalisa Buffo, Enrica Boda and Silvia Di Maria.