Neuroendocrinology 1/2017
NADPH-Diaphorase Colocalizes with GPER and Is Modulated by the GPER Agonist G1 in the Supraoptic and Paraventricular Nuclei of Ovariectomized Female Rats
Grassi D. a-f , Lagunas N. a, b , Pinos H. a , Panzica G.C. d, e , Garcia-Segura L.M. b , Collado P. a
Nitric oxide is produced in the brain by the neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) and carries out a wide range of functions by acting as a neurotransmitter-like molecule. Gonadal hormones are involved in the regulation of the brain nitrergic system. We have previously demonstrated that estradiol, via classical estrogen receptors (ERs), regulates NOS activity in the supraoptic (SON) and paraventricular (PVN) nuclei of the hypothalamus, acting through both ERα and ERβ.
Magnocellular and parvocellular neurons in the SON and PVN also express the G protein-coupled ER (GPER).
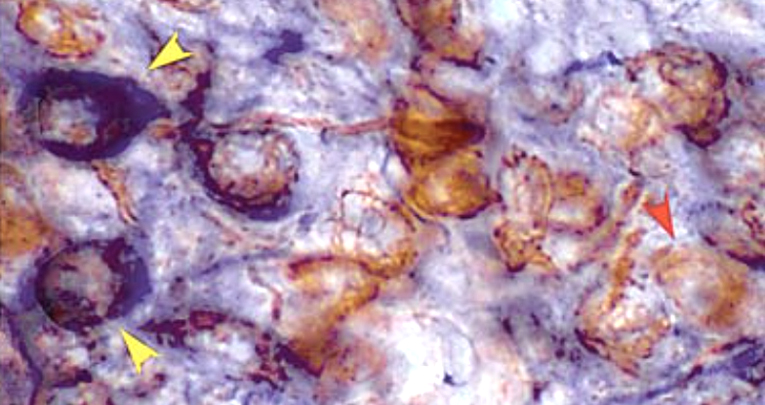
In this study, we have assessed whether GPER is also involved in the regulation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH)-diaphorase in the SON and PVN. Adult female ovariectomized rats were treated with G1, a selective GPER agonist, or with G1 in combination with G15, a selective GPER antagonist. G1 treatment decreased NADPH-diaphorase expression in the SON and in all PVN subnuclei.
The treatment with G1 + G15 effectively rescued the G1-dependent decrease in NADPH-diaphorase expression in both brain regions. In addition, the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2, one of the kinases involved in the GPER-dependent intracellular signaling pathway and in NOS phosphorylation, was assessed in the same brain nuclei. Treatment with G1 significantly decreased the number of p-ERK 1/2-positive cells in the SON and PVN, while the treatment with G1 + G15 significantly recovered its number to control values.
These findings suggest that the activation of GPER in the SON and PVN inhibits the phosphorylation of ERK 1/2, which induces a decrease in NADPH-diaphorase expression.
>> read more