21/08/2016
Scientific Reports, August 2016
Pellegrino RM
1,2
, Boda E
3,4
, Montarolo F
4
, Boero M
1,2
, Mezzanotte M
1,2
, Saglio G
1,2
, Buffo A
3,4
, Roetto A
1,2
The Transferrin Receptor 2 (Tfr2) modulates systemic iron metabolism through the regulation of iron regulator Hepcidin (Hepc) and Tfr2 inactivation causes systemic iron overload.
Based on data demonstrating Tfr2 expression in brain, we analysed Tfr2-KO mice in order to examine the molecular, histological and behavioural consequences of Tfr2 silencing in this tissue. Tfr2 abrogation caused an accumulation of iron in specific districts in the nervous tissue that was not accompanied by a brain Hepc response.
Moreover, Tfr2-KO mice presented a selective overactivation of neurons in the limbic circuit and the emergence of an anxious-like behaviour. Furthermore, microglial cells showed a particular sensitivity to iron perturbation. We conclude that Tfr2 is a key regulator of brain iron homeostasis and propose a role for Tfr2 alpha in the regulation of anxiety circuits.
>> read more
1
Department of Clinical and Biological Sciences, University of Torino, Turin, Italy.
2
AOU San Luigi Regione Gonzole 10043 Orbassano Turin, Italy.
3
Department of Neuroscience Rita Levi-Montalcini, University of Torino, Turin, Italy.
4
Neuroscience Institute Cavalieri Ottolenghi Regione Gonzole 10043 Orbassano Turin, Italy.
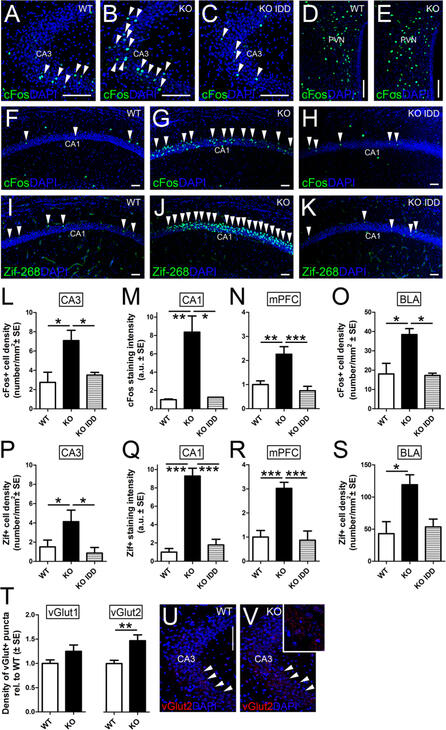
Activity-related immediate early genes in anxiety circuits.
The immediate early genes cFos (
A
–
H
) and Zif-268 (
I
–
K
) are upregulated in neurons of the CA1 (
F
,
G
) and CA3 (
A
,
B
) areas of
Tfr2
-KO mice compared to WT brains, while no increase in positive cells occurs in the PVN (
D
,
E
). Quantifications of the number of positive nuclei over the area of the corresponding layers show that cFos+ or Zif-268+ cells significantly increased in mutant mice in standard conditions while they return to control levels in mutant fed with IDD diet (
H
,
K
,
L
,
M
,
P
,
Q
).
This very same trend is found in the mPFC and BLA (
N
,
O
,
R
,
S
). (
T
–
V
) Quantifications of glutamatergic terminals in CA3 (red in (
U
,
V
)) show that vGlut2+ puncta are higher in number in
Tfr2
-KO mice, while vGlut1+ ones do not differ from WT. Asterisks refer to statistically significant differences: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Scale bars: 100 μm, IDD, iron deficient diet; IED, iron enriched diet; PVN, periventricular hypothalamic nucleus; mPFC, medial prefrontal cortex; BLA, basolateral amygdala; error bars, standard error of the mean.